Rice is one of the important food crops on this globe and feed almost half of the world’s population. Rice is good source of basic human needs nutrients, vitamins and minerals as well an excellent source of carbohydrates. It’s is an estimate that every ten people on this globe eat rice as staple food.Rice production is extremely labouredly task and using large amount of water. It’s an estimated that 1 kg of rice production required 1000 liter of water in case of sustainable utilization of water but it will increase many fold in case of low standards practices of irrigation. Rice production process divided into three stages:
Every stage has specific concern that a good farmer must consider for sustainable and high production. Concern face at every stage divided into three categories:
- High: Top priority concern that mainly determine the health, production and quality of the produce
- Medium: Medium level concern but must consider for good production
- Low: Low level concern not affect the crop much extend but must consider during crop production it will increase intensity of damage when multiple low risk concerns combine
Fallow Stage:
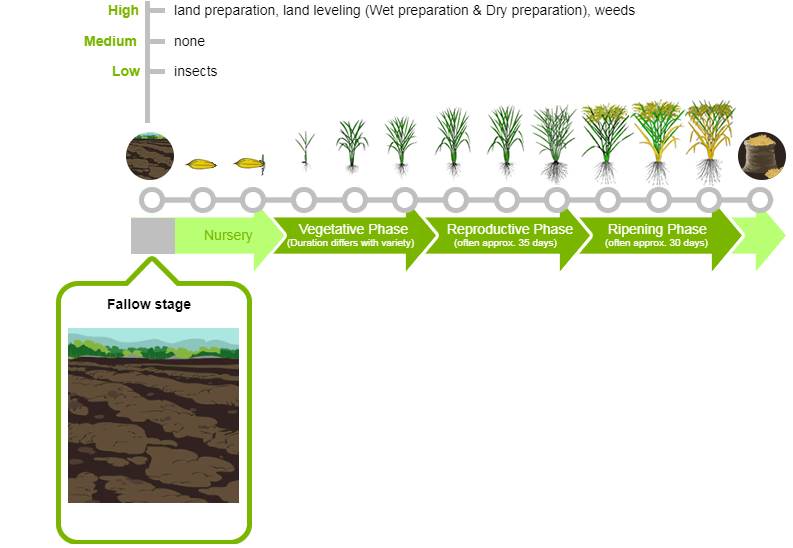
Fallow stage is the period between two crops cycle like period between wheat and rice. After and before harvesting of one crop the land is fallow till the cultivation of second crop. Fallow stage is very important for soil fertility It gives a resting period to soil and after this resting period soil/land is going to ready for next crop. If farmer not give a little rest to soil it will results low performance of land during next crop cycle. The main concerns during fallow stage are:
- High: land preparation, land leveling, Wet preparation, Dry preparation and weeds control
- Medium: None
- Low: Insect problems
Nursery Stage
Nursery stage is starting point of rice cultivation; it’s very crucial stage of rice that determine the final production and economical value of the produce. The main concerns are:

Seeds Stage
Seeds stage is very important during nursery stage, seeds determine the number of seedlings in the field and proper number of seedling transplanted in the field will directly determine the final paddy yield.
- High: Selection of variety, germination rate , Snail attack, birds issue, rodents problem and water issue
- Medium: None
- Low: Nutrition and Insects problem
Germination
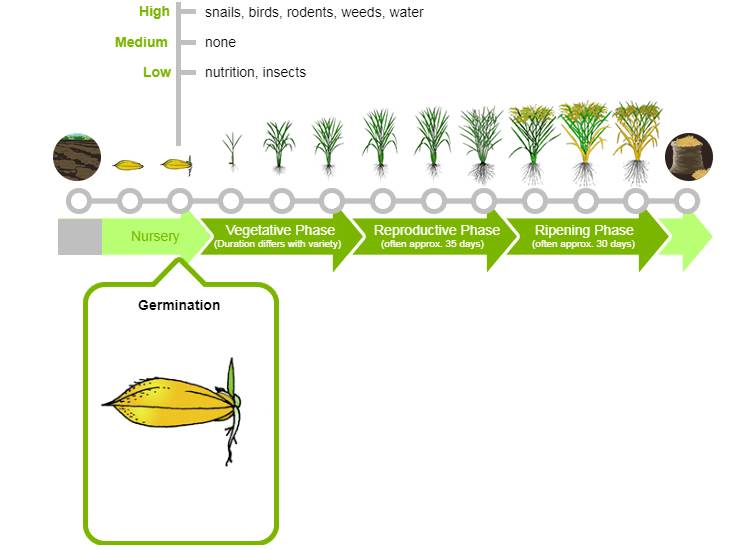
Germination percentage reflects the sprouting of viable seeds. Viability of the seeds depends on following concern:
- High: Selection of variety, germination rate , Snail attack, birds issue, rodents problem and water issue
- Medium: None
- Low: Nutrition and Insects problem
Development or Field Stage
Rice seedling transplanted into field after 14-21 days of nursery preparation. Before nursery transplanted land is leveled and prepared for transplantation. After transplantation in field rice development phases start. Development phases divided into three phases:

- Vegetative Phase (60 days or depend on variety)
- Reproductive Phase (30 days)
- Ripening Phase (30 days)
Vegetative Phase
The longest phase during development is vegetative phase which is lasted 60 or more days depend on rice variety. During vegetative plants developed tillers (side branches) and ready for next step of reproductive phase. Vegetative phase further divide into following sub-stages:
Seedling Stage:
This stage started just after transplantation of rice from nursery to prepared land. Main stem start dividing into sister stem termed as tillers. Following concerns are considers during seedling stage:
- High: Snail and Weeds issue
- Medium: Nutrition and Water management
- Low: Birds, rodents and insects problem
Tillering Stage
Tillering stage start just after development of first side branch termed as tiller. We can consider as general rule of them

“The yield of paddy is directly proportional to number of tillers produced per hill or plant”
Hence, more number of tillers means more spikes and more spike finally having more number of grains. Following concerns are considers during tillering stage:
- High: Weeds issue is one of the main concern of this stage
- Medium: Nutrition and Water management
- Low: Insects and disease
Stem elongation
Stem elongation is the stage of growth of rice plant after complete formation of tillers. Following concerns are considers during stem elongation stage:

- High: None
- Medium: Weeds, Nutrition and Water management
- Low: Insects and disease
Reproductive Phase
Reproductive phase is very crucial phase in rice life cycle. The events happen in reproductive phase include:
Booting Stage

Booting stage refer to the spike development stage after stem elongation. Spikes are structure that will be the platform of flowering and grains in future. Following concerns are considers during booting stage:
- High: Nutrition management
- Medium: Insects and Water management
- Low: Weeds and disease management
Flowering stage
The main event of flowering stage is formation of flowers on spike that developed during booting stage. The event of pollination occurs after development of flowers on spike. Following concerns are considers during flowering stage:

- High: Water management
- Medium: None
- Low: Rodents, insects and diseases management
Ripening Phase
Ripening phase a series of stages from milky stage to mature stage. Ripening phase divided into three stages:
Milk Stage
Grains formation just starts after pollination. Grains formation started from the development of milky substance and this stage referred as milk stage. Following concerns are considers during milk stage:

- High: Water management
- Medium: Birds can damage milky grain and like to feed sweet grains
- Low: Rodents, insects and diseases management
Dough stage
Dough stage referred transformation of milky substance inside the newly developed grain to hard jelly like substance technically term as dough. Following concerns are considers during Dough stage:

- High: Birds are main pest at this stage and damage seeds
- Medium: None
- Low: Rodents, insects and diseases management
Mature Stage
After the series of changes rice grain now converted into hard mass technically called seeds or grain. Following concerns are considers during mature stage:
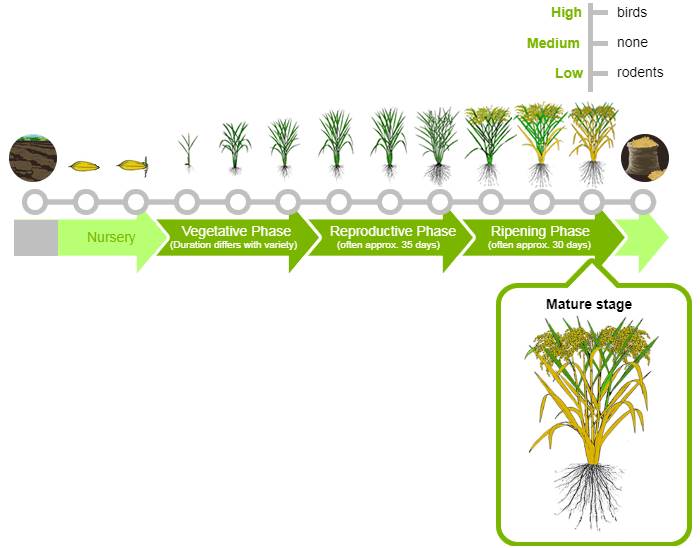
- High: Birds are main pest at this stage and damage seeds
- Medium: None
- Low: Rodents Problems
Harvesting and Storage
Harvesting and storage is the final stage of the paddy life cycle. Rice is harvest at appropriate moisture level in case of harvesting having high moisture leads to the development of fungus and Aflatoxin in grain, and made them unsafe for human consumption.

After harvesting storage is final stage for the paddy, if storage is not carefully arrange all harvested crop maybe completely loss. Following concerns are considers during harvesting and storage stage:
- High: Rodents, insets and water
- Medium: None
- Low: Birds, weeds and diseases

